You may not have any symptoms. Sometimes a doctor may suspect a tumor only after treatment with antibiotics doesnt cure the pneumonia.
 Lung Cancer Booklet Roche Bangladesh Limited
Lung Cancer Booklet Roche Bangladesh Limited
Symptoms if cancer has spread to your lymph nodes Lymph nodes are part of a system of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluid and fights infection.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/non-small-cell-lung-cancer-symptoms-4588803_final_CORRECTED-bb05e218504e4d3788bd7e5a2d99d3a7.png)
Tumor on lung symptoms. Chest pain especially when taking deep breaths. Normal lung tissue surrounds this small round. Signs and symptoms of lung cancer may include.
A lung NET is much less likely to cause carcinoid syndrome than a GI tract NET. Lung metastases or metastatic cancer to the lung occurs when a cancer that originates in another area of the body such as the breast or bladder spreads to the lungs. But lymph nodes also get bigger if you have an infection.
Symptoms of lung cancer may include. Instead it causes symptoms Pancoast syndrome related to invasion of surrounding tissues in its unique location at the apex of the lung. A cough that does not go away or gets worse Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum spit or phlegm Chest pain that is often worse with deep breathing coughing or laughing.
Its caused by hypercalcaemia - where the body retains too much calcium. In cases where the carcinoid cannot be completely removed palliative surgery may be performed to remove most of the tumor or to relieve symptoms. Changes to the voice such as hoarseness.
Losing weight without trying. Learn the signs and symptoms how to treat it and what the outlook is for someone who has it. Post-obstructive pneumonia which is when a tumor blocking a large air passage causes an infection.
Coughing or spitting up blood. The most common symptom if cancer has spread to the lymph nodes is that they are usually bigger than normal. More than 90 of nodules are found by accident when you get a chest X-ray or CT computed tomography scan for some other reason.
Signs and symptoms of lung cancer typically occur when the disease is advanced. Many lung carcinoid tumors can be treated with surgery alone except in cases where the tumor has spread to other organs. What are the symptoms of benign lung tumors.
Most carcinoid tumors start in the large bronchial tubes leading into the lung. Large carcinoids can cause partial or complete blockage of an air passage which can lead to pneumonia an infection in the lung. Symptoms of lung cancer develop as the condition progresses.
Cough which can sometimes be bloody. Chest infection that lasts more than three weeks or keeps coming back. Mild cough that lasts for a long time.
A cough that doesnt go away after 2 or 3 weeks a long-standing cough that gets worse. A new cough that does not go away. Shortness of breath or becoming easily winded are also possible symptoms of lung cancer.
A new cough that doesnt go away. Metastatic or secondary lung cancer starts in another part of your body but spreads to your lungs. Cough with or without bloody sputum or phlegm.
Together these symptoms are called Horner. Coughing up blood even a small amount. Most people with lung metastases do not have symptoms but they may experience a cough chest pain or hemoptysis.
The most common symptoms of lung cancer are. Although a Pancoast tumor is a lung tumor it rarely causes symptoms that are typically related to the lungs for example cough and chest pain. If you do have symptoms they may include.
Changes in breathing can occur if lung cancer blocks or narrows an airway or if fluid from a lung tumor. A nodule is a spot on the lung seen on an X-ray or computed tomography CT scan. People with a lung NET may experience the following symptoms or signs.
The main symptoms of lung cancer include. Tumors at the top of the lungs can affect facial nerves leading to drooping of one eyelid small pupil or lack of perspiration on one side of the face. Lung cancer symptoms include a cough that wont go away coughing up blood difficulty breathing and having an ache or pain while breathing.
In fact a nodule shows up on about one in every 500 chest X-rays. Lung cancer typically doesnt cause signs and symptoms in its earliest stages. Between 10 and 20 percent of all lung cancer patients develop gastrointestinal symptoms it said.
Shortness of breath difficulty breathing wheezing.
Surgical excision of the tumor was done. Terminology of giant cell tumors is inconsistent in literature Epidemiology.
 Giant Cell Tumor Of The Tendon Sheath Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Giant Cell Tumor Of The Tendon Sheath Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
A benign nodular tumor that is found on the tendon sheath of the hands and feet.
Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath. It involves the joint fluid sac tendon sheath and synovial membrane of the joints. Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath of the toe imitating macrodactyly. Less frequent than localized type Usually.
Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath. TGCT tumors often develop from the lining of joints. Foot Ankle Int 24868-702003.
Chassaignac first described these benign soft-tissue masses. Malignant giant cell neoplasm. Ultrasound shows a well-defined solid lesion which is free from the tendons.
Most cases occur in the hand where local recurrence after excision has been reported in up to 40 of cases. A young female presented with a lump in distal forearmwrist region on the palmar side. Several hypotheses were formulated about the etiological factors of these tumors but still there is not a common opinion on etiology prognostic factors and recurrence rate.
Tenosynovial giant cell tumors TSGCTs are a group of rare benign tumors that involve the synovium bursae and tendon sheath. Malignant giant cell tumor. Pigmented villonodular synovitis giant-cell tumor of the tendon sheath and synovial membrane.
Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath is the most common form of giant cell tumors and is the second most common soft tissue tumor of the hand region after ganglion cyst. A review of eighty-one cases. This group of tumors can be divided into different subsets according to their site growth pattern and prognosis.
The current standard treatment of choice is simple excision. Report of 15 cases. Giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath are the second most common tumors of the hand with simple ganglion cysts being the most common.
Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath with intraosseous invasion. Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath is a rare solitary benign soft tissue tumor which may arise in the tendon sheath tissues around the ankle and the toes of the foot. Second most common soft-tissue tumor seen in the hand following ganglion cyst.
Skaliczki G Mady F. Age 40 years with female predominance. Giant cell tumors GCTs of the tendon sheath are the second most common tumors of the hand with simple ganglion cysts being the most common.
J Hand Surg 23A732-61998. Synovium is the thin layer of tissue or membrane that covers the inner surface of the joint spaces and the bursae and tendon sheaths. Localized TGCT is sometimes referred to as giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath.
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is the term used in the latest 2013 World Health Organization classification 1011. It is grouped with the chondro-osseous tumours. Uriburu IJF Levy VD.
Diffuse TGCT is also called. Page views in 2021 to date. Intraosseous growth of giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath localized nodular tenosynovitis of the digits.
The giant cell tumor of tendon sheath GCTTS is the most common benign neoplasm in the hand after the ganglion cyst. Page views in 2020. Giant cell tumour of tendon sheath is a relatively common tumour of small joints.
Tenosynovial giant cell tumor is a group of rare typically non-malignant tumors of the joints. Other diagnostic terms used for this lesion include nodular or diffuse pigmented villonodular tenosynovitis xanthogranuloma benign synovioma and fibrous histiocytoma of tendon sheath or synovium. Magnetic resonance imaging is the diagnostic tool of choice for both diagnosis and treatment planning.
Giant Cell Tumor of the Tendon Sheath Giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath are the second most common tumors of the hand with simple ganglion cysts being the most common. GCT of tendon sheath is a circumscribed tumor that does not always arise from the tendon sheath but may arise from the synovium. Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath.
Malignant giant cell neoplasm of the tendon sheath. They have previously been known as giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath GCTTS pigmented villonodular tumor of the tendon sheath PVNTS extra-articular pigmented villonodular tumor of the tendon sheath or localized or focal nodular synovitis 11. These tumors were first characterized by Chassaignac in 1852.
Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath is also named tenosynovial giant cell tumor. Main Recent Top Doctors. It is abbreviated GCT of tendon sheath.
Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath is defined as a benign reactive lesion which is similar to PVNS. Common symptoms of TGCT include swelling pain stiffness and reduced mobility in the affected joint or limb. Histopathology revealed the lesion being a giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath.
A Giant Cell Tumor of Tendon Sheath GCTTS is a benign tumor consisting of many types of polygonal cells in a bed of collagen. Giant cell tumor of tendon sheath or synovium nodular tenosynovitis is a common tumor that may present as either localized or diffuse disease. Also known as pigmented villonodular tumor of the tendon sheath PVNTS Epidemiology present in 3rd-5th decade of life.
A malignant neoplasm characterized by then presence of atypical giant cells. Giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath most commonly occur in patients in the third to fifth decades of life. 1 Chassaignac first described these benign.
Fibroma of tendon sheath abbreviated FTS redirect to this article.
You may experience dizzy spells or get confused about where you are and whats happening. You will be given activity restrictions which allows your body time to recover and heal from your surgery.
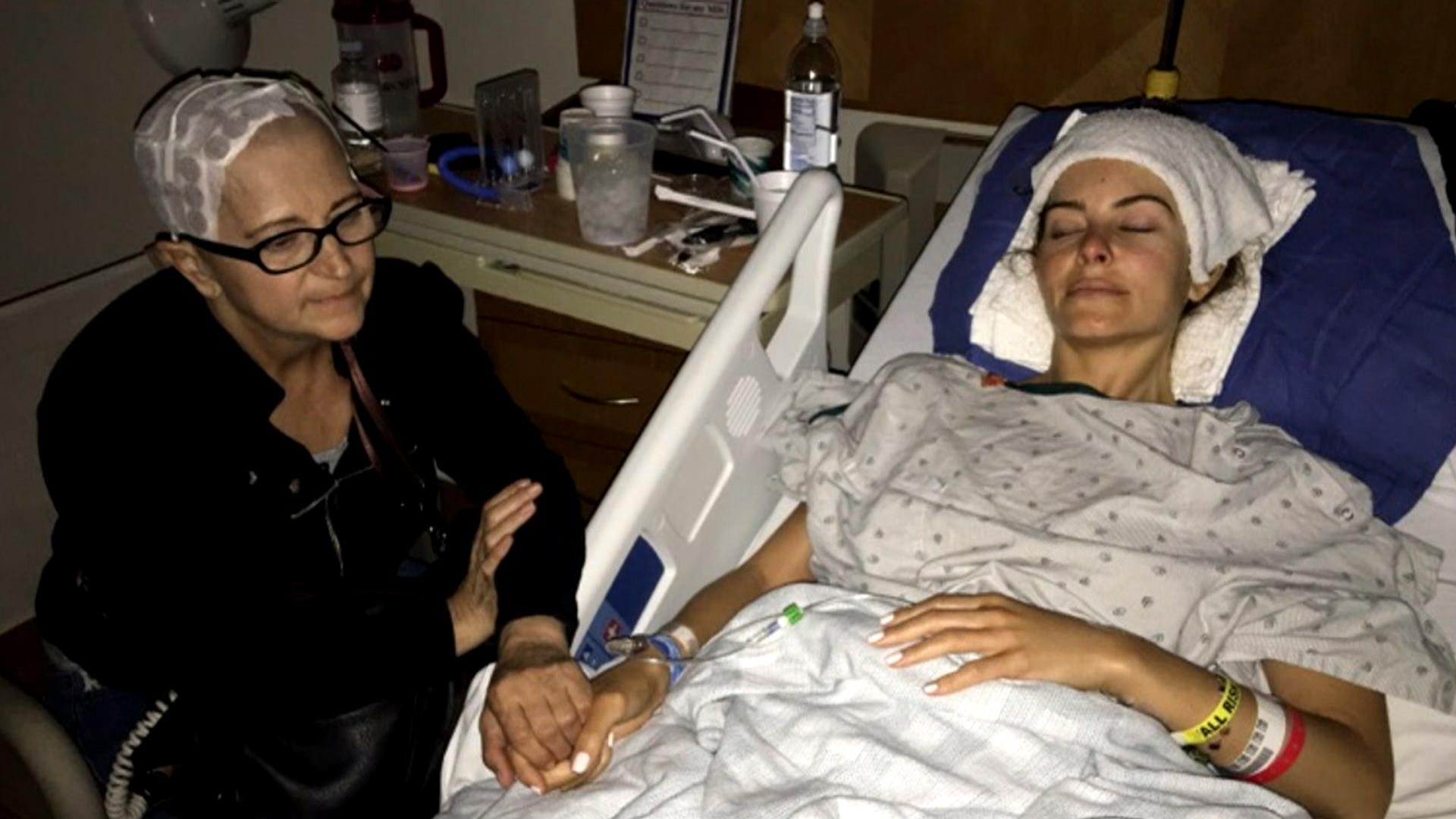 Maria Menounos Shares Brain Tumor Symptoms Year After Surgery
Maria Menounos Shares Brain Tumor Symptoms Year After Surgery
My doctor said Theres something there.

Brain tumor removal surgery recovery. A brain tumor surgery is often the primary treatment suggested by doctors for removing tumors from the brain without causing any serious damage. It depends on the condition of the patient. Fatigue and lethargy are common reactions to surgery and people who experience post-surgery neurological issues may need extra support during this time to manage those problems.
For the first week following surgery you will be prescribed steroids to reduce inflammation in the brain and some patients also require anti-epilepsy medications. Your Recovery at Home Once your brain tumor specialist determines you are in stable condition you will be released from the hospital to recover at home. Your caregiver may also experience stress difficulty sleeping anxiety and other indirect symptoms.
In fact patients might feel worse than they did before the surgery. Resting is a normal process of recovery that will help your body recuperate. After all the focus at this point is the brain tumor surgery recovery period.
Extreme care and recovery is mandatory after any brain tumor surgery to ensure your overall well being. A Variable Recovery Process After Surgery Following brain tumor surgery patients are moved to an intensive care unit where nurses and physicians carefully monitor brain function and vital signs while trying to ascertain any deficits or complications. The following information may provide peace of mind for patients and their caregivers.
There are different types of surgeries that can be performed for treating a brain tumor. Expect to spend 2-3 days recovering in the hospital though your stay may be longer if you have any complicating health factors. Getting surgery to remove a brain tumor can take a toll on your body so it may take some time to get back to your regular activities.
Generally speaking you can have the following expectations. Full recovery takes about 2 months. Frederick Lang MD and Jeffrey Weinberg MD neurosurgeons at MD Anderson Cancer Center answer frequently asked questions about what to expect when y.
Because of your personal health factors and the differences between types of tumors your benign brain tumor surgery recovery is going to be a very individual process. Recovering from brain tumour surgery. Once the neurosurgery is over it will take time for you to regain your original level of energy.
After the procedure the physician anesthesiologist may provide medications to address potential side effects of brain surgery such as seizures or nausea. Non-cancerous tumors are mostly treated with a brain tumor surgery. While you are asleep you might be breathing through a machine called ventilator.
Brain Tumor Surgery Recovery Time. Patients who undergo surgery for brain cancer may need to be patient during recovery. After metastatic brain cancer surgery patients typically return gradually to normal activities within a week or two.
But sometimes your surgeon might decide to keep you asleep for a few days after surgery to help you recover. The procedure used to remove the brain tumor. Swelling in the brain after an operation means it will take some time before you feel the benefit from having your tumor removed.
The amount of time required to recover after brain surgery is different for each person and depends on. After brain surgery it will take time for the patient to return to hisher usual level of energy. How much time to recover.
Everyone takes a different amount of time to recover. Brain surgery is a lot for your body to cope with. After Brain Tumor Surgery Before Treatment Brain surgery is a lot for the body to handle and you will likely experience some side effects as you recover.
If your surgeon is only performing a biopsy the surgery typically takes 2-3 hours. You might stay in hospital for around 3 to 10 days after surgery. Make sure you pay attention to your bodys needs and dont overexert yourself if you feel tired.
They use sedatives to keep you asleep. If your surgeon is performing a craniotomy and removal of your tumor the surgery typically takes 4-6 hours. How long you stay in hospital depends on your operation and how long you take to recover.
Care and Recovery after Brain Surgery. Recovery from brain tumor surgery is a time-consuming process that takes about 4 weeks and sometimes more. It can take some time to recover from your brain tumour operation.
If your surgeon using a transsphenoidal approach to remove your tumor the surgery typically takes 3-4 hours. Any surgery will be performed in a hospital setting and require a stay of up to one week. Plenty of rest is needed to provide adequate healing time for the brain tissues.
Your physician anesthesiologist will also work to maintain healthy brain blood flow blood pressure and oxygenation levels in addition to providing pain control. You have a 5-centimeter tumor in your cerebellum she recalls. There are many types for brain tumor surgeries to be performed and many other treatments for the brain tumor than open brain surgery.
Heather Wright will never forget the moment she learned that her headaches and occasional bouts of left leg weakness were caused by a brain tumor. Healing requires extra rest. Most people wake up a few hours after their brain surgery.
For the purposes of this article the writer will assume that this was an open brain surgery. These episodes can come and go and are a normal part of the recovery period.