PraderWilli syndrome PWS and Angelman syndrome AS are clinically distinct complex disorders mapped to chromosome 15q11q13. Mild to moderate intellectual impairment and behavioral problems are also typical of.
 Prader Willi Syndrome And Angelman Syndrome In Cousins From A Family With A Translocation Between Chromosomes 6 And 15 Nejm
Prader Willi Syndrome And Angelman Syndrome In Cousins From A Family With A Translocation Between Chromosomes 6 And 15 Nejm
PraderWilli syndrome PWS is a genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15.

Prader willi and angelman syndrome. Prader-Willi syndrome PWS and Angelman syndrome AS are diseases that are both caused by a deletion in the same region of chromosome 15 namely 15q11-q13. PraderWilli syndrome PWS and Angelman syndrome AS are two distinct neurogenetic disorders in which imprinted genes on the proximal long arm of chromosome 15 are affected. They are only discussed together because they share a similar and uncommon genetic basis.
PWS has many associated genes. Causes mental retardation and Hyperphagia excessive eating. Neonates with PWS are hypotonic have a weak cry and are poor feeders but improve over time.
AS is caused by the loss of function of maternally inherited genes within 15q112-q13 due to deletion paternal uniparental disomy ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A UBE3A gene variants imprinting defects translocation defects or unknown causes. 1 st International Genetic Reference Panel for Prader Willi and Angelman Syndromes The panel comprises six human genomic DNA samples to cover a range of Prader Willi and Angelman syndrome genetic defects. Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome PWS and AS respectively are two clinically distinct conditions often discussed together due to both diseases involving uniparental disomy and genomic imprinting on the same chromosome 15.
An older term happy puppet syndrome is generally considered pejorative. Although the SNORD116 gene cluster has become a prime candidate for PWS it cannot be excluded that other paternally expressed genes in the chromosomal region 15q11q13 contribute to the full phenotype. They both have characteristic neurologic developmental and behavioral phenotypes plus other structural and functional abnormalities.
Angelman syndrome AS and Prader-Willi syndrome PWS are complex neurodevelopmental genetic disorders characterized by developmental delay and intellectual disability. Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes are 2 clinically distinct disorders associated with multiple anomalies and mental retardation. Males and females are affected with equal frequency.
Both Prader-Willi and Angelman syndrome are neurodevelopmental disorders that are associated with intellectual disabilities in patients. Angelman is usually UBE3A. Angelman and Prader-Willi syndrome have both a defect in chromosome 15.
Both PWS and AS involve abnormality in the section 15q11-q13 of this chromosome. Prader-Willi syndrome PWS and Angelman syndrome AS are distinct mental retardation syndromes caused by paternal and maternal deficiencies respectively in chromosome 15q11-q13. Prader-Willi Syndrome involves inheriting a mutated allele from the father while the allele inherited from the mother is naturally silenced.
Angelman Syndrome involves inheriting a mutated allele from the mother while the allele inherited from the father is naturally silenced. What is Angelman syndrome. If the abnormal chromosome comes from the father paternal you get Prader-Willi syndrome.
Both conditions are on chromosome 15 but are not reciprocal imprintsUPDs of the same gene. Prader-Willi syndrome PWS is a congenital disorder characterized by a biphasic clinical course. PraderWilli syndrome is a separate condition caused by a similar loss of the fathers chromosome 15.
PraderWilli syndrome PWS and Angelman syndrome AS are two distinct neurogenetic disorders in which imprinted genes on the proximal long arm of chromosome 15 are affected. But if the abnormal chromosome comes from the mother maternal baby get Angelman a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by severe intellectual and developmental disability. They involve genes that are located in the same region in the genome and are characterized by genetic imprinting.
Although the SNORD116 gene cluster has become a prime candidate for PWS it cannot be excluded that other paternally expressed genes in the chromosomal region 15q11q13 contribute to the full phenotype. Prader-Willi syndrome maternal imprinting or maternal UPD. Due to methylation patterns however different genes are responsible for the two syndromes.
It is named after British pediatrician Harry Angelman who first described the syndrome in 1965. In newborns symptoms include weak muscles poor feeding and slow development. Angelman syndrome paternal imprinting or paternal UPD.
Approximately 70 of these patients have a large deletion of approximately 4 Mb extending from D15S9 ML34 through D15S12 IR10. In later infancy and childhood individuals with PWS have global developmental delay short stature hypogonadism small hands and feet and marked hyperphagia leading to obesity. Angelman syndrome AS and Prader-Willi syndrome PWS are examples of disorders that can be caused by uniparental disomy.
Most PWS patients are within the mild IQ range while those with Angelman syndrome usually have severe intellectual abnormalities. Beginning in childhood those affected become constantly hungry which often leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes. People with Angelman syndrome AS have an unusual facial appearance short stature severe intellectual disability with a lack of speech stiff arm movements and a spastic uncoordinated walk.
Although the SNORD116 gene cluster has become a prime candidate for PWS it cannot be excluded that other paternally expressed genes in the chromosomal region 15q11q13 contribute to the full phenotype. Samples are presented as 5 µg freeze dried genomic DNA in glass ampoules. Prader-Willi syndrome PWS and Angelman syndrome AS are two distinct neurogenetic disorders in which imprinted genes on the proximal long arm of chromosome 15 are affected.
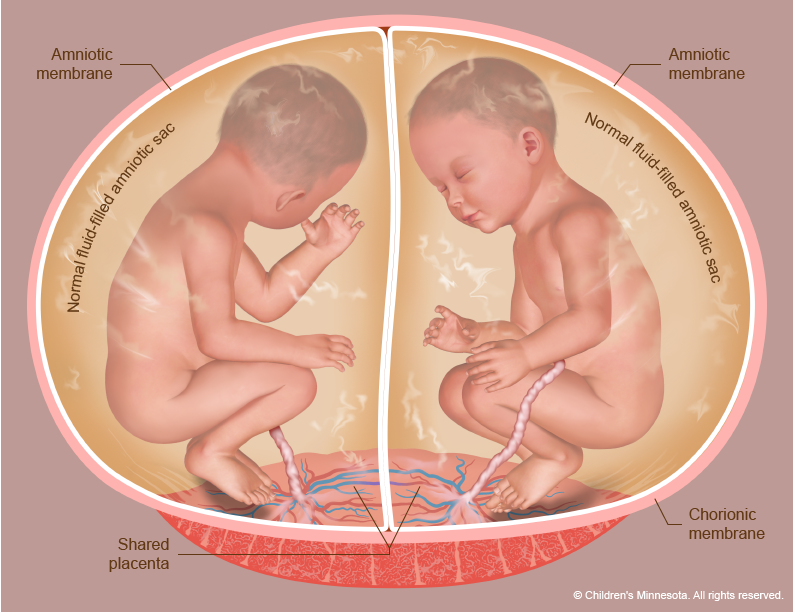
Please see links below for critical steps to take when you find out you are pregnant with multiples and diagnosed. Monochorionic twin pregnancies are monitored for development of twin-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS with ultrasound examination every two weeks beginning at 16 weeks of gestation and continuing until the mid-third trimester.
 Twin To Twin Transfusion Syndrome Ttts Treatment
Twin To Twin Transfusion Syndrome Ttts Treatment
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome results when there is intrauterine blood transfusion from 1 twin donor to the other twin recipient.

Twin to twin transfusion syndrome. The shared placenta contains abnormal blood vessels which connect the umbilical cords and circulations of the twins. These pregnancies are known as monochorionic. Twin-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a rare serious condition that can occur in pregnancies when identical twins share a placenta.
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a severe complication of monochorionic twinning. And the other called the recipient develops high. Twin to twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a condition that occurs only in monochorionic pregnancies ones in which two or more genetically identical babies usually twins share the same placenta.
The twins do not have malformations but one transfuses the other through abnormal or imbalanced blood vessel connections in the shared placenta. We want to help you immediately. It can affect monochorionic multiples that is multiple pregnancies where two or more fetuses share a chorion and hence a single.
You can email or message us on social media but if it is urgent please call. This happens when blood is transferred from on baby to the other through blood vessels within a shared placenta monochorionic. Both infants may have problems depending on how much blood is passed from one to the other.
TTTS affects identical twins or higher multiple gestations who share a common monochorionic placenta. Most cases of TTTS present in the early second trimester and are staged according to the Quintero system table 1. Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome TTTS is a serious progressive disorder.
The Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome helps families 24 hours a day 7 days a week in all time zones. Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome TTTS affects approximately 15 of identical twins that share a placenta. The twin that loses the blood is called the donor twin.
When twins share a single placenta we call them monochorionic. One twin called the donor becomes dehydrated. Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome or TTTS is a disease of the placenta not the babies.
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS also known as feto-fetal transfusion syndrome FFTS twin oligohydramnios-polyhydramnios sequence TOPS and stuck twin syndrome is a complication of disproportionate blood supply resulting in high morbidity and mortality. The condition occurs when blood from one twin commonly called the donor is transfused into the other twin commonly called the recipient via blood vessels in the shared placenta. The twin that receives the blood is called the recipient twin.
Usually each twin will have its own sac of amniotic fluid and its own umbilical cord connecting it to the placenta. This occurs when the blood vessels of the babies shared placenta are connected. Twin to twin transfusion syndrome is a condition that affects approximately 10 per cent one in ten of identical twins that share a single placenta.
Twin to twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a rare condition that occurs during a twin pregnancy when blood moves from one twin the donor twin to the other the recipient twin while in the womb. Abnormal blood vessel connections form in the placenta and allow blood to flow unevenly between the babies. Twin to twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a disease of the placenta or afterbirth that affects identical twin pregnancies.
What is twin-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS Twin-twin transfusion syndrome also called TTTS or twin to twin transfusion syndrome is a condition in which the blood flows unequally between twins that share a placenta monochorionic twins. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a rare pregnancy condition affecting identical twins or other multiples. Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome Twin to twin transfusion syndrome or TTTS is very rare and occurs only in identical mono-zygotic twins.
Detailed testing to measure amniotic fluid volume bladder filling and blood flow in the recipient and donor twins can be conducted by a maternal-fetal medicine specialist to confirm the diagnosis. It affects twins or other multiples that share a single placenta with blood vessels that go from one baby to the other. Although all identical twins share a placenta TTTS develops in about 10 to 15 percent of those pregnancies.
If TTTS is left untreated mortality is 80-100 in severe cases. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome can be suspected by a doctor based on the results of routine prenatal ultrasound. TTTS occurs in pregnancies where twins share one placenta afterbirth and a network of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients essential for development in the womb.
1 TTTS is a complication that specifically occurs in identical monozygotic twin pregnancies that share the same egg sac monochorionic that. Twin to twin transfusion syndrome TTTS is a serious disorder that occurs in identical twins and higher-order multiples who share a placenta. In about 15 of cases a shared vessel causes an unequal exchange of blood.
This results in one baby this twin is referred to as the recipient receiving more blood flow while the other baby this. TTTS occurs in about 10 to 15 percent of monochorionic diamniotic two amniotic sacs twins. Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome TTTS occurs when the blood supply of one twin moves to the other through the shared placenta.
1 F Fetoscopic laser photocoagulation.
Alternatively HELLP syndrome can be classified on the basis of platelet count nadir. A wide range of non-specific symptoms may be present in women with HELLP syndrome.
 Pin By Wendy Owens On Step 2 Maloooooo Hellp Syndrome Syndrome Elevated Liver Enzymes
Pin By Wendy Owens On Step 2 Maloooooo Hellp Syndrome Syndrome Elevated Liver Enzymes
Sibai Criteria 1993 Abnormal peripheral smear schistocytes LDH 600 UL.
Hellp syndrome lab results. 1Clinique de Gynecologie et dObstetrique Universite de Goettingen Allemagne. A 39-year-old G2P1001 female presented from an outside hospital following an eclamptic seizure in the setting of HELLP syndrome. Pain in the upper right or middle of the abdomen.
HELLP syndrome is a life-threatening obstetric complication usually considered to be a variant or complication of pre-eclampsia. HELLP Syndrome is a life- threatening syndrome that stands for. Hemolysis or the destruction of red blood cells Elevated Liver Enzymes and Low Platelet count.
Some theorize that because HELLP is a variant of preeclampsia the pathophysiology stems from a common sourceIn preeclampsia defective placental vascular remodeling during weeks 16-22 of pregnancy with the second wave of trophoblastic invasion into the decidua results in inadequate placental perfusion. Abdominal or chest tenderness and upper right upper side pain from liver distention. It is a devastating illness that typically occurs in the third trimester of gestation.
HELLP syndrome a variant of severe preeclampsia and defined by the following. However the fi rst published article naming the syndrome as HELLP. Pregnant women developing HELLP syndrome have reported experiencing one or more of these symptoms.
LDH or bilirubin with hemolysis as evidenced on abnormal. The physical symptoms of HELLP Syndrome may seem at first like preeclampsia. There also may or may not be extra protein in the urine.
Infant respiratory distress syndrome lung failure Blood transfusion. Article in French Kuhn W1 Rath W Loos W Graeff H. It was proposed that HELLP syndrome occurs in a circulatory inflammatory milieu that might in turn.
Low Platelets count. Symptoms may include fatigue. Nursing Study Guide on HELLP Syndrome.
Diagnostic Criteria for HELLP Syndrome Hemolysis Elevated Liver Enzymes Low Platelets. Class II 50000 to less than 100000 per mm 3 50 to. Elevated Liver enzymes Serum AST 70 UL.
AST or ALT levels of 70 IUL or more. Class I less than 50000 per mm 3 50 10 9 per L. The infant morbidity and mortality rate is anywhere from 10-60 depending on many factors such as gestation of pregnancy the severity of symptoms and the promptness of treatment.
Clinical and laboratory test results. For 12 hours required. Platelet count of 100000mL or less.
Symptoms of HELLP Syndrome. The pathophysiology of HELLP syndrome is ill-defined. HELLP syndrome is a group of symptoms that can develop in pregnant women.
Innate and adaptive immune involvement in hemolysis elevated liver enzymes and low platelet HELLP syndrome is an understudied field although it is of high clinical importance. HELLP Syndrome NCLEX Review Care Plans. HELLP syndrome is a disorder of the liver and blood that can be fatal if left untreated.
Complete HELLP syndrome is characterized by the following. Symptoms are wide-ranging and. Martin Criteria 1991 LDH 600 UL.
Lactate dehydrogenase 600 UL. 14-17 Introduction HELLP syndrome was fi rst described by Pritchard et al in 1954 1. We present a unique case of complicated post-partum HELLP syndrome.
Fluid retention and excess weight gain. HELLP syndrome is diagnosed when laboratory tests show hemolysis burst red blood cells release hemoglobin into the blood plasma elevated liver enzymes and low platelets. The platelet count a peripheral blood smear AST ALT bilirubin and LDH are required for the diagnosis of HELLP syndrome.
The patient was a 34-year-old Caucasian G1PO woman at 40 weeks gestational age who presented for induction of labor. Platelet count. Nauseavomitingindigestion with pain after eating.
The maternal mortality rate is about 11 with HELLP syndrome. This syndrome implies a risk of serious morbidity and mortality to both the mother and the fetus during pregnancy. And rarely nosebleed or seizures.
Symptoms may include feeling tired retaining fluid headache nausea upper right abdominal pain blurry vision nosebleeds and seizures. The greater the laboratory abnormalities the greater the clinicians. It usually begins during the last three months of pregnancy or shortly after childbirth.
HELLP Syndrome is a rare and serious condition that occurs during pregnancy and can last after childbirth. HELLP syndrome is a complication of pregnancy characterized by hemolysis elevated liver enzymes and a low platelet count. Platelet count.
HELLP syndrome haemolysis liver enzymes platelet count hypertension liver distension pre-eclampsia N Z J Med Lab Sci 2010. We report the work-up and intraoperative and postoperative management of this complex patient with multiple medical needs. HELLP syndrome is characterized by hemolysis elevated liver enzymes and thrombocytopenia.
The Hellp syndrome is a complication of toxemia. May take longer based on weather holiday or lab delays. May take longer based on weather holiday or lab delays.
This condition was complicated by intrauterine fetal demise and disseminated intravascular coagulation which required an emergent cesarean section. Indirect bilirubin 12 mgdL.
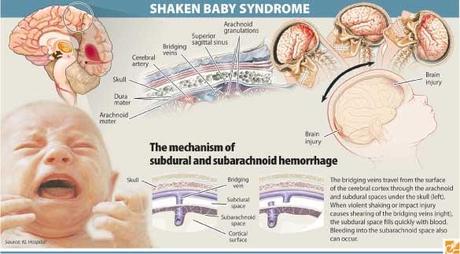
Complications include seizures visual impairment cerebral palsy and cognitive impairment. Often there are no visible signs of trauma.
 Shaken Baby Syndrome Those Who Survive Are Horribly Afflicted
Shaken Baby Syndrome Those Who Survive Are Horribly Afflicted
Pregnancy And Baby Care Articles Toddler Illness.
Consequences of shaken baby syndrome. It is one of the most common causes of disability and death in adults. Neurologic side effects of either shaking or blunt skull trauma may span from developmental delays seizure disorders visual impairment and blindness to death. TBI is a broad term that describes a vast array of injuries that happen to the brain.
The constellation of these injuries does not occur with short falls seizures or as a consequence of vaccination. Children who have been shaken may have learning disabilities cognitive impairment speech or behavioral problems eating or sleeping disorders loss of vision blindness deafness and epilepsy. Symptoms may include vomiting or a baby that will not settle.
Long Term Effects of Shaken Baby Syndrome. Shaking a baby or young child can cause their brain to repeatedly hit the inside of the skull. Of those that survive up to 50 end up with serious and irreversible damage.
Abusive brain trauma causes lifelong harm to the brain and sometimes leads to death. It is difficult to diagnose abusive head trauma only through the symptoms accurately. Traumatic brain injury TBI happens when a sudden external physical assault damages the brain.
The long-term effects or prognosis of the shaken baby syndrome include physical and cognitive disabilities. Orthopedic consequences of inflicted trauma range from the need for recurrent surgery to permanent loss of function if the back and thus spinal cord is involved. Here are the few shaken baby syndrome risk factors.
Death is usually caused by uncontrollable increased intracranial pressure from cerebral edema bleeding within the brain or tears in the brain tissue. Other problems include impaired brain functions sensory functions and even neurological disorders like cerebral palsy. Shaken baby syndrome is a form of child abuse.
As a result there is damage to the brain and hemorrhages under the membranes of the brain without external signs of damage. Shaken baby syndrome is preventable. The prognosis for victims of shaken baby syndrome varies with the severity of injury but generally is poor.
The violent shaking of shaken baby syndrome can cause severe brain injury disabling that child forever. This causes swelling bruising and bleeding in the brain. Problems with speech learning memory and focus.
Symptoms may range from subtle to obvious. The child may be further injured if he or she is thrown down onto a surface which is known as shaken impact syndrome. Shaken baby syndrome injuries are the result of violent trauma.
Shaken baby syndrome SBS is a complex of organic disorders that can occur if the childs body experiences a concussion. When a baby is shaken hard by the shoulders arms or legs it can cause learning disabilities behavior disorders vision problems or blindness. A problem in moving parts of the body.
What are the consequences of shaken baby syndrome. The shaken baby syndrome can also have significant effects on a childs future development. Shaken baby syndrome is a form of child abuse that can result in permanent brain damage or death.
The child sustained diffuse brain injuries responsible for spastic right hemiplegia leading to secondary orthopaedic consequences as well as severe cognitive impairment worsening over time. Poor eyesight or blindness. Shaken Baby Syndrome What is traumatic brain injury.
Shaken baby syndrome SBS also known as abusive head trauma AHT is an injury to a childs head caused by someone else. Infant can also suffer acceleration and deceleration injuries. Lasting after effects of shaken baby syndrome or SBS leave the child with severe brain damage as well as lifelong disabilities.
Shaken baby syndrome SBS is a type of brain injury that occurs when a baby or a toddler is shaken violently. Some of the consequences can be blindness cerebral palsy intellectual disability epilepsy difficulties with language etc. The babys head dangles causing the membranes of brain cells to rupture.
The developmental quotient measured at 15 months of age was 55 and worsened as age increased. Help is available for parents who are at risk of harming a child. At 6 years and 8 months the childs IQ had fallen to 40.
Many cases are fatal or lead to severe neurological deficits. Shaken baby syndrome destroys a childs brain cells and prevents his or her brain from getting enough oxygen. One in every 10 children who suffer from this type of brain injury end up dying.
This impact can trigger bruising in the brain bleeding in the brain and brain swelling.
TSS gets worse very quickly and can be fatal if not treated promptly. The bacteria produce toxins that can quickly lead to organ failure and even death.
 Toxic Shock Syndrome Symptoms Causes And Diagnosis
Toxic Shock Syndrome Symptoms Causes And Diagnosis
It is caused when the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus gets into the bloodstream and produces toxins.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/toxic-shock-syndrome-4175808-5c5db70646e0fb0001ca86cf.png)
What is toxic shock syndrome. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is an uncommon but serious life-threatening complication of certain types of infections. Its caused by the release of toxins from an overgrowth of bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus or staph which is found in many. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is rare but it can be life-threatening so its important to know its signs and symptoms so you can spot it and treat it quickly.
Its often associated with tampon use in young women but it can affect anyone of any age including men and children. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a cluster of symptoms that involves many systems of the body. Toxic shock syndrome is a rare but serious medical condition caused by a bacterial infection.
TSS is typically caused by bacteria of the Streptococcus pyogenes or Staphylococcus aureus type though others. Toxic shock syndrome was first identified in 1978 when a group of children became ill with it. Women who have their period are menstruating are most likely to get TSS as it is thought to be associated with tampon use.
It is a multi-system disease that presents with organ failure in addition to fever rash hypotension and skin manifestations. These bacteria live on the skin anyway but if they get deeper. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a rare but potentially life-threatening condition that is caused by certain strains of bacteria that produce toxins poisons.
Certain bacterial infections release toxins into the bloodstream which then spreads the toxins to body organs. Symptoms may include fever rash skin peeling and low blood pressure. Toxic shock syndrome can be defined as an acute illness caused by toxin-producing bacteria.
Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a rare but life-threatening complication of bacterial infection or colonization. What is toxic shock syndrome. This can cause severe damage and illness.
What is toxic shock syndrome. Often toxic shock syndrome results from toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus staph bacteria but the condition may also be caused by toxins produced by group A streptococcus strep bacteria. Since TSS puts out toxins into your.
Toxic shock syndrome is a rare life-threatening complication of certain types of bacterial infections. This bacterium produces a toxin termed TSS toxin-1 TSST- or phage-group-1 streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. TSS can affect anyone male or female.
It can result in the failure of vital organs such as the liver lungs or heart. It is caused by either staph Staphylococcus aureus bacteria or strep Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria. Toxic shock syndrome is a rare life-threatening illness triggered by certain bacteria group A streptococcal and Staphylococcus aureus.
It generally is characterized by high fever with or without chills a sunburn-like rash and shock low blood pressure andor very high heart rate. Toxic shock syndrome is caused by toxins produced by the staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a potentially fatal bacterial infection that puts the body into a state of shock resulting in organ failure.
Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a rare and potentially life-threatening illness that is thought to be caused by infection with certain types of bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Toxic shock syndrome is a sudden potentially fatal condition. What is Toxic Shock Syndrome.
Toxic Shock Syndrome is caused by toxins produced by certain types of staphylococcus bacteria and it causes fevers shock and organ issues. In toxic shock syndrome toxins poisons produced by the bacteria cause a severe drop in blood pressure hypotension and organ failure. What is toxic shock syndrome.
Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a condition caused by bacterial toxins. The symptoms of TSS can manifest two to four days after. Toxic shock syndrome TSS is a rare but life-threatening condition caused by bacteria getting into the body and releasing harmful toxins.
There may also be symptoms related to the specific underlying infection such as mastitis osteomyelitis necrotising fasciitis or pneumonia. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that TSS affects an average of one in 100000 people in the US but this doesnt mean its any less severein fact it can be deadly. Toxic shock syndrome is a severe illness associated with group A Streptococcus GAS or Streptococcus pyogenes.
TSS is the medical term for a set of characteristic symptoms that appear when a bacterial infection occurs in the body the bacteria in question being Group A streptococcus sometimes referred to. TSS was first described in 1978 in children but subsequent reports identified TSS outbreaks in women who use tampons.