Hepatitis B virus HBV hepatitis C virus HCV human immunodeficiency virus HIV. Its estimated that only about 18 percent of occupational exposures to HCV lead to an.
 14 Needle Stick Injuries Among Health Care Workers
14 Needle Stick Injuries Among Health Care Workers
The major blood-borne pathogens of concern associated with needlestick injury are hepatitis B virus HBV hepatitis C virus HCV and HIV.

Hepatitis c needle stick. Your chances of catching a disease from a single needle stick are usually very low. We present the case of a 29-year-old medical intern who sustained a needlestick injury from a source patient known to be infected with both human immunodeficiency virus and HCV. The estimated risk for infection after a needlestick injury or cut exposure to HCV-infected blood is approximately 18.
117 The risk oftransmission from a needlestick exposuredepends upon the concentration of HCV RNA inthe blood of the source patient and the volume ofthe inoculum. None developed hepatitis and anti-HCV testing by a second-generation. Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses I HTLV-I and II HTLV-II.
Several preliminary studies suggest that treatment of hepatitis C in the acute phase could significantly reduce the rate of chronicity. Hepatitis C virus HCV. 114-116 This is less than the risk of hepatitis B virustransmission from a hepatitis B-positive sourcebut higher than the risk of HIV transmissionfrom an HIV-positive source.
After needlestick injury from a known positive HCV patient source the risk of seroconversion is approximately 18. When administered within 24 hours of. It depends upon the quantity of RNA In the fluid and after exposure you have to wait for few weeks to get yourself tested for hepatitis C and if the test comes positive then interferon therapy should be started.
However the risk of contracting hepatitis C due to something like a needle stick is still rather low. Numerous prospective studies have evaluated the post-exposure effectiveness of HBIG. When interferon has been authorized for this indication and if effectiveness is confirmed treatment might be recommended for health personnel with acute needle-stick transmitted HCV infection.
There is a significant rate of hepatitis C co-infection in those who are HIV positive particularly in intravenous drug users with 82 of HIV infected individuals also co-infected with hep C 13. A needlestick injury is the penetration of the skin by a hypodermic needle or other sharp object that has been in contact with blood tissue or other body fluids before the exposure. The bottom line of this article is that the risk of transmission of hepatitis C after having a needle stick injury from a hepatitis C-positive patient is low.
However PEP is not recommended for hepatitis C virus HCV exposures. Even though the acute physiological effects of a needlestick injury are generally negligible these injuries can lead to transmission of blood-borne diseases placing those exposed at increased risk of infection from disease causing pathogens such as the hepatitis B virus hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficie. Needlestick injuries are an occupational hazard of many healthcare workers including nurses anaesthetists dentists and laboratory technicians.
The management for occupational HIV or hepatitis B virus exposures includes postexposure prophylaxis PEP when necessary. HCP might be exposed to blood or other body fluids by injury from a used needle or from a splash of blood or body fluids into the eye or mouth while caring for a patient. Currently 380 000400 000 occupational exposures to blood-borne pathogens occur annually in the United States.
No HCV vaccine has been developed. The case patient subsequently developed acute HCV infection. No post-exposure prophylaxis is available for hepatitis C.
The major blood-borne pathogens of concern associated with needlestick injury are. The case patient subsequently developed acute HCV infection. Hepatitis C virus HCV transmission following a needlestick is an important threat to health care workers.
Hepatitis C virus HCV transmission following a needlestick is an important threat to health care workers. Needlestick injury is a wound piercing the skin caused by a contaminated sharps instrument most commonly a hypodermic needle. Several studies revealed an overall 02 risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries.
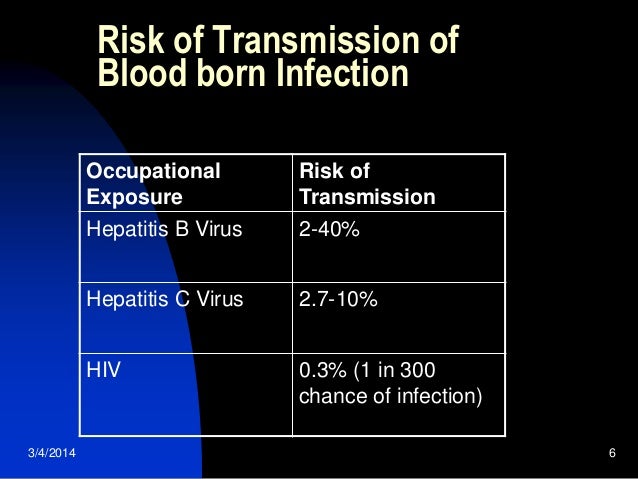
Hepatitis C HCV information includes statistics transmission symptoms treatment and guidelines about hepatitis C testing and diagnosis. The risk of transmission of HCV after a needlestick exposure from a hepatitis C-positive source is estimated at between 2-10. According to the CDC some 385000 health care workers accidentally stick themselves with needles every year.
To assess the risk to hospital personnel of acquiring an hepatitis C virus HCV infection as a result of occupational exposure to needle-stick injuries 81 employees who had parenteral exposure to an anti-HCV- positive source were followed for 12 months. Infected needle-stick victims might be followed by having their transaminases checked 4-12 weeks later. However other infectious agents also have the potential for transmission through needlestick injury including.
For these scenarios consult with the Infectious. However other infectious agents also have the potential for transmission through needlestick injury. Only the highest risk needlestick injuries are offered HIV post-exposure prophylaxis which consists of 2-3 anti-retroviral medications administered for 28 days.
We present the case of a 29-year-old medical intern who sustained a needlestick injury from a source patient known to be infected with both human immunodeficiency virus and HCV. Exposure to hepatitis viruses has long been recognized as an occupational risk for health care personnel HCP and recommendations previously were established for managing occupational exposures to bloodborne pathogens including hepatitis C virus HCV 1 Supplementary Figure httpsstackscdcgovviewcdc90288. Hepatitis B booster vaccines can be given by the LMO.
No PEP is available.