The esophagus is the tube that carries food and liquid to your stomach. Esophageal cancer may be due to either esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ESCC or adenocarcinoma EAC.
Start here to find information on esophageal cancer treatment causes and prevention screening research and statistics.
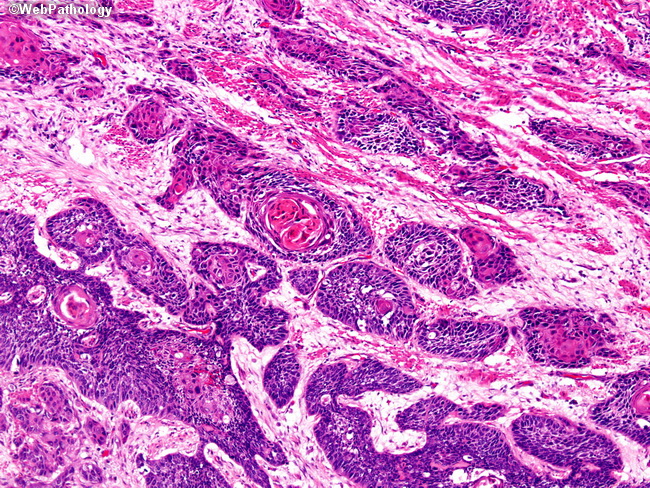
Squamous cells in esophagus. N0 No cancer cells are seen in any of the lymph nodes examined. Recent studies have shown that NOTCH mutations are commonly seen in human ESCC. Primary squamous cell thyroid carcinoma shows an aggressive biological phenotype resulting in poor prognosis for patients.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma SCC of Esophagus is a highly-malignant tumor of the epithelium. Squamous cell carcinoma starts in the cells that line the esophagus. Squamous Throat Cancer Survival Rate Throat cancer or squamous carcinoma of the amygdala is a part of the head and neck cancers.
Squamous cell esophagus cancer accounts for up to 95 percent of all cases of esophagus cancer worldwide. Esophageal cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the esophagus. The most common staging system for SCC of the esophagus is the TNM system.
These forms of esophageal cancer develop in some parts of the esophagus and are driven by genetic changes. Squamous cell carcinoma SCC of the esophagus is staged differently than adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Causes and risk factors for squamous cell carcinoma of the throat include.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most prevalent esophageal cancer worldwide. This chapter summarizes our current understanding of the NOTCH pathway in normal esophagus and in ESCC. Esophageal cancer EC is one of the most common malignancies worldwide 1 2There has been a dramatic rise in the incidence of EC in the developed world over the last 30 years The vast majority of ECs occur as either squamous cell carcinomas ESCCs or adenocarcinomas 4 5ESCCs account for approximately 90 of EC cases 4 5.
Squamous cells are the flat cells that line different internal parts of the body including the esophagus. Here we obtain a detailed immune cell atlas of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ESCC at single-cell resolution. For SCC of the esophagus there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4.
We present three cases of esophageal squamous papillomas identified histologically. Their prevalence is estimated to be less than 001 in the general population. N1 Cancer cells are seen in one or two lymph nodes.
SCCs tend to occur closer to the mouth while adenocarcinomas occur closer to the stomach. The most common types of esophageal cancer are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Esophageal squamous papillomas are rare epithelial lesions typically discovered incidentally during EGD.
We present three cases of esophageal squamous papillomas identified histologically. Esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas ESCC which are similar to head and neck cancer in their appearance and association with tobacco and alcohol consumptionand esophageal adenocarcinomas EAC which are often. The esophagus is a part of the upper gastrointestinal tract and is also known as the food-pipe.
The throat consists of the pharynx the upper part behind the tongue and the larynx the voice box. It may be possible to identify these lesions macroscopically. Esophageal squamous mucosa is a normal condition of a healthy esophagus as most of the esophagus is actually lined with squamous mucosa or squamous cells according to the American Cancer Society.
Squamous cell cancer arises from the cells that line the upper part of the esophagus. Their prevalence is estimated to be less than 001 in the general population. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I II III and IV.
Some rare forms of esophageal cancer include small cell carcinoma sarcoma. The squamous cells are flat thin cells that line the surface of the esophagus. Esophageal cancer is malignancy of the esophagus.
The esophagus or food pipe is a tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach and is responsible for the passage of food from the. Squamous cell carcinoma is given a nodal stage between 0 and 3 based on finding cancer cells in a lymph node and the number of lymph nodes involved. Nodal stage pN for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus.
In oncology cancers of the squamous cells of the head and neck are often considered together because they share many similarities in the incidence the type of cancer the predisposing factors the pathological characteristics the Cancer treatment and the. These cells are called squamous cells. Exhausted T and NK cells regulatory T cells Tregs alternatively activated.
It may be possible to identify t. Epithelia are tissues consisting of cells closely juxtaposed without intervening intercellular substances. The Squamous epithelial cells Are thin flat cells found in layers or sheets that cover surfaces such as the skin and the lining of blood vessels and the esophagus.
There are two types of esophageal cancer. This type of cancer can occur anywhere in the esophagus. Squamous cell carcinoma occurs most often in the upper and middle portions of the esophagus.
Squamous cells are also found on the surface of the skin and are flat with an appearance similar to fish scales. Esophageal squamous papillomas are rare epithelial lesions typically discovered incidentally during EGD. Esophageal cancers are typically carcinomas that arise from the epithelium or surface lining of the esophagusMost esophageal cancers fall into one of two classes.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the throat is the most common type of throat cancerSquamous cell carcinoma of the throat is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells of the lining of the throat. Epithelia are avascular but all epitheliagrowin an underlying layer of vascular connective tissue. One study provided a positive predictive value of 88.
There are various subtypes primarily squamous cell cancer and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma ESCC is a deadly disease that requires extensive research on its mechanisms prevention and therapy. Adenocarcinoma arises from glandular cells that are present at the junction of the esophagus and stomach.
The Regeneration center has helped many lung cancer patients by using. However the new treatments raise many questions.
 The Different Mirnas Regulate Properties Of Lung Cancer Stem Cells Download Scientific Diagram
The Different Mirnas Regulate Properties Of Lung Cancer Stem Cells Download Scientific Diagram
The widely embraced cancer stem cell CSC theory has also been applied for lung cancer postulating that an often small proportion of tumor cells with stem cell properties are responsible for tumor growth therapeutic resistance and metastasis.

Lung cancer stem cells. Non-small cell lung cancer. Among the cell types that can be used for this purpose mesenchymal stem cells MSCs are considered as promising source of stem cells in personalized cell-based therapies. Stem cell-based therapies exhibit profound therapeutic potential for treating various human diseases including cancer.
In treating diseases such as lung cancer it is essential to consider all your choices. However in multiple myeloma and some types of leukemia the stem cell transplant may work against cancer directly. Cui F Wang J Chen D et al.
How Stem Cell Transplants Work against Cancer. A549 and H1299 human lung cancer cell lines were obtained from the Stem Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Bidlingmaier S Zhu X Liu B.
Information about the treatment protocol oncology treatment center or facility as well as the doctors and resident physicians. Small cell lung cancer occurs almost exclusively in heavy smokers and is less common than non-small cell lung cancer. CD133 is a temporary marker of cancer stem cells in small cell lung cancer but not in non-small cell lung cancer.
We have also identified a subpopulation of stem cells in the lung that is responsible for generating pre-malignant lung cancer lesions. Cancer stem cell CSC theory refers to a subpopulation of cancer cells also named tumor-initiating cells that can drive cancer development. Yan X Luo H Zhou X et al.
We hypothesize that the interaction between the stem cells in the blood and the stem cells in the lung are critical to prevent lung cancer. J Mol Med Berl 2008861025-32. Initially reported in haematological malignancies and subsequently in several solid tumours CSC represent potential therapeutic targets and several strategies are already in clinical development.
Non-small cell lung cancers include squamous cell carcinoma adenocarcinoma and large cell carcinoma. The utility and limitations of glycosylated human CD133 epitopes in defining cancer stem cells. Cells presenting these characteristics have been identified and isolated from lung cancer.
This happens because of an effect called graft-versus-tumor that can occur after allogeneic transplants. Cui F Wang J Chen D et al. Non-small cell lung cancer is an umbrella term for several types of lung cancers.
Instead they help you recover your ability to produce stem cells after treatment with very high doses of radiation therapy chemotherapy or both. Stem Cell Treatments for Cancer If you have leukemia or lymphoma you may need a stem cell transplant. As we learn more about the therapeutic potential of stem cells and other cell therapies in clinical trials of non-lung diseases we hope to be able to move toward further consideration of these approaches in lung diseases.
The cancer stem cell CSC hypothesis suggests that tumors are arranged in a hierarchical structure with the presence of a small subset of stem-like cells that are responsible for tumor initiation and growth. Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths despite recent breakthroughs in immunotherapy. Identification of CD90 as a marker for lung cancer stem cells in A549 and H446 cell lines.
Cells were cultured with Dulbeccos modified Eagle medium DMEM supplemented. They also let your body recover faster. Small cell lung cancer SCLC cells are missing a surface protein that triggers an immune response allowing them to hide from one of the bodys key cancer defenses a new study suggests.
CD133 is a temporary marker of cancer stem cells in small cell lung cancer but not in non-small cell lung cancer. Other research into stem cell therapies has. Stem cell treatments for lungs are showing promise for treating lung diseases most notably COPD and non-small cell lung cancer which does not metastasize nearly as quickly as small cell lung cancer.
Lung cancer stem cells Conventional anti-cancer therapies kill the bulk of the tumor however CSCs exhibit robust intrinsic resistance and survive therapy due to increased telomere length activation of anti-apoptotic pathways increased membrane transporter activity and their ability to migrate and metastasize. Termed cancer stem cells CSC these cells are believed to be a phenotypically distinct population that possesses tumourigenic potential. These cells help replace cells damaged by the cancer.
T-Cell Immunotherapy Stem Cell Treatment for Lung Cancer. Mounting research shows that stem cells can also make a difference in pulmonary fibrosis. In contrast to the slow improvement in lung cancer prevention and treatment pulmonary stem cell biology driven by mouse models is rapidly revealing progenitor cell populations throughout lungs 4 5.
Stem cells are young enough that they can still grow up to become any number of specialized cells potentially including mature lung tissue cells. Stem cell transplants do not usually work against cancer directly. Stem Cell Therapy Advisory The use of stem cells for treating lung diseases has great appeal.
The birth of the cell marked the passage from pre-biotic chemistry to partitioned units resembling modern cells. Leeuwenhoek in 1674 What microscope is used to observe a small living organism in a lab.
 Cell Unit Test Review Cp Biology L1 Ppt Download
Cell Unit Test Review Cp Biology L1 Ppt Download
Who was the first scientist who described living cells as seen through a simple microscope.

The scientist who first described living cells. The scientist who first studied living cell was AV. A contrast or optical microscope. Hooke was one of the earliest scientists to study living things under a microscope.
Median response time is 34 minutes and may be longer for new subjects. Robert Hooke 16351703 was the first to describe cells based upon his microscopic observations of cork. No one created the cell as all living things have cells and a creator of the cell would have to not.
This article focuses on the 50 most influential scientists alive today and their profound contributions to science. The first time the word cell was used to refer to these tiny units of life was in 1665 by a British scientist named Robert Hooke. The first man to witness a live cell under a microscope was Anton van Leeuwenhoek who in 1674 described the algae Spirogyra.
The cells of plants and algae have a hard ____ ____ made of cellulose. Scientist who first described cell. Updated January 13 2020 Robert Hooke July 18 1635March 3 1703 was a 17th-century natural philosopheran early scientistnoted for a variety of observations of the natural world.
German scientists Theodore Schwann and Mattias Schleiden studied cells of animals and plants respectively. This illustration was published in his work Micrographia. But perhaps his most notable discovery came in 1665 when he looked at a sliver of cork through a microscope lens and discovered cells.
These are scientists who have invented the Internet and fiber optics challenged AIDS and cancer developed new drugs and in general made crucial advances in medicine genetics astronomy ecology physics and computer programming. However Schwann and Schleiden misunderstood how cells grow. He was the one that came up with cell 1 0.
A scientist who observed that cork was composed of tiny hollow boxes that he called cells. To preform particular jobs in the body. What are the three parts of the cell theory.
Although English Scientist Robert Hooke described a honeycomb-like network of cellulae Latin for little storage rooms in cork slice using his primitive compound microscope the first man to clearly observe a live cell under a microscope was Anton van Leeuwenhoek who in 1674 described the algae Spirogyra. In this theory the internal contents of cells were called protoplasm and described as a jelly-like substance sometimes called living jelly. Van Leeuwenhoek probably also saw bacteria.
Provide examples of. The microscopes of his day were not very strong but Hooke was still able to make an important discovery. 1All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms 3All cells come from preexisting cells.
He made thin slices of cork and likened the boxy partitions he observed to the cells small rooms in a monastery. The first cell theory is credited to the work of Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in the 1830s. Although Robert Hooke was the first to see any cells but they were dead and from cork.
The origin of cells was the most important step in the evolution of life on Earth. The cell walls observed by Hooke gave no indication of the nucleus and other organelles found in most living cells. Formulation of the Cell Theory.
Scientific description of all living. These scientists identified key differences between the two cell types and put forth the idea that cells were the fundamental units of both plants and animals. Structure performing a specific function with in a cell.
Many years later Robert Brown discovered the nucleus the engine that makes a cell function. Leewenhoek the first scientist to describe living cells as seen through a simple microscope. Energy converting organelle found in plant and algae cells.
The first wet cell was invented in 1800 by an Italian scientist named Allesandra Volta. He saw living algae in pond water. What cell structures best reveal evolutionary unity.
Although it was the scientist Robert Hooke who coined the term cell after observing dead cells through his microscope it was Anton van Leeuwenhoek who first observed live cells. The English scientist Robert Hooke first used the term cells in 1665 to describe the small chambers within cork that he observed under a microscope of his own design. English physicist and microscopist Robert Hooke 16351702 first described cells in 1665.
The final transition to living entities that fulfill all the definitions of modern cells depended on the ability to evolve effectively by natural. The open spaces Hooke observed were empty but he and others suggested these spaces might be used for fluid transport in living plants. The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 using a microscope.
Response times vary by subject and question complexity. Who was the first scientist to describe living cells as seen through a simple microscope.
T helper cells T H cells assist other lymphocytes including maturation of B cells into plasma cells and memory B cells and activation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophagesThese cells are also known as CD4 T cells as they express the CD4 on their surfaces. Helper T cells become activated when they are presented with peptide antigens by MHC class II molecules which are expressed on the.
 Characterization Of Subsets Of Cd4 Memory T Cells Reveals Early Branched Pathways Of T Cell Differentiation In Humans Pnas
Characterization Of Subsets Of Cd4 Memory T Cells Reveals Early Branched Pathways Of T Cell Differentiation In Humans Pnas
This is mostly due to the fact that CD4 T cells tend to expand far less in response to antigenic stimuli thereby thwarting attempts at their detection during the course of an.

Cd4 memory t cells. Pathway analysis revealed a differentiation trajectory associated with cellular activation and proinflammatory effector functions. CD4 T cell help is required for the generation of CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte CTL memory. In contrast with B cells we find no decisive.
Antigen-specific memory T cells specific to viruses or other microbial molecules can be found in both T CM and T EM subsets. IL-2 deficient cells are more effective than wild-type memory cells on a per cell basis at combating IAV and drive tempered early innate inflammatory responses. CD4 T cells are known to be important for maintenance of effector T Eff and memory T memory CD8 T cells 5 therefore we determined whether adoptive transfer of both pmel and TRP1 T cells increased the number and frequency of T memory and T Eff pmelCD8 T cells compared to adoptive transfer with pmel alone.
Functional differentiation and homeostasis. MP CD4 cells have been used as surrogates for Ag-specific memory CD4 cells in studies of T cell homeostasis with the assumption that the two types of cells are interchangeable 9 19To test the validity of this supposition we directly compared the acute homeostatic turnover of both types of cells in irradiated B6 hosts for 1 wk. Stockinger B1 Bourgeois C Kassiotis G.
Memory T cells are either CD4 or the virus-specific CD8 depending on the type of antigen encountered MacLeod et al 2010. Airway memory CD4 T cells are the first cells to encounter viral antigen during respiratory infections suggesting a key role in protection. In the respiratory tract memory CD4 T cells include cells in the airway and parenchyma and cells adhering to the pulmonary vasculature.
CD4T cells recognise peptides presented on MHC class II molecules which are found on antigen presenting cells APCs. MP CD4 cells are a heterogeneous population of cells. CD4 as well as CD8 T cells can be subdivided into naive central memory CM effector memory EM and terminal differentiated effector memory TEMRA populations based on phenotype namely the expression of lymph node homing receptors and CD45 splice variants as well as activation requirements and functional differences.
Bstockinimrmrcacuk CD4 T cells are central regulators of both humoral and cellular immune responses. CD4 T-cell memory is in some ways more enigmatic than CD8 T-cell memory. The memory T cells are quickly converted into large numbers of effector T cells upon reexposure to the specific invading antigen thus providing a rapid response to past infection.
While much is known about the effector function of Th cells in combating pathogens and promoting autoimmune diseases the roles and biology of memory CD4 Th cells are complex and less well understood. Although most information is currently based on observations in the cytotoxic T cells CD8-positive subset similar populations appear to exist for both the helper T cells CD4-positive and the cytotoxic T cellsPrimary function of memory cells is augmented. 1Division of Molecular Immunology The National Institute for Medical Research Mill Hill London UK.
Immunological memory without a memory T cell Eric B. Unlike TE cells TM cells have a low rate of metabolism unless they are activated by reencountering cognate antigen. Here we use genome-wide analyses to show how CD4 T cell help delivered during priming promotes memory.
Bell1 and Jurgen Westermann2 1Faculty of Life Sciences Immunology Section University of Manchester Manchester M13 9PT UK 2Institue for Anatomy University of Lubeck 23538 Lubeck Germany Immunological memory crucially depends on CD4 T cells. As a whole they play a major role in instigating and shaping adaptive immune responses. CD4 memory T cells on trial.
CD4 memory T cells. CD4 T helper Th cells play central roles in immunity in health and disease. Memory-like CD4 T cells had high expression of Ki-67 indicative of cell division and CD5 a surrogate marker of TCR avidity and produced the cytokines IFN-g and IL-2.
The Central Memory CD4 T Cell Isolation Kit was developed for the isolation of central memory CD4 T cells from human PBMCs in a two-step procedureCentral memory CD4 T cells are isolated based on the expression of CD197 CCR7 and the absence of CD45RA on these cells. CD4 central memory T cells play a critical role in the pathogenesis of simian immunodeficiency virus disease and the CCR5 density on the surface of CD4 T cells is an important factor in human. Author summary We show that memory CD4 T cell mediated protection against influenza A virus is independent of the signature multifunctional cytokine IL-2 that is thought to define the most protective memory cells.
Th1-polarised cells are responsible for control of intracellular pathogens such as viruses and some bacteria. Microbiota-reactive CD4 T memory TM cells are generated during intestinal infections and inflammation and can revert to pathogenic CD4 T effector TE cells resulting in chronicity of inflammatory bowel disease IBD. Furthermore CD4 T cell clones in the infant intestine are highly compartmentalized and have limited overlap with clones in the spleen or blood Bunders et al 2012 suggesting that the intestine might harbor a distinctive tissue-resident population of memory CD4 T cells prior to birth.
However it is not clear whether airway and parenchymal cells differentially mediate protection during respiratory. In human autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis MS there is a critical need to better understand the.
In fact one of the criteria for a lupus diagnosis is actually the opposite. A count of over 11000 WBC per microliter of blood is considered high.
 High White Blood Cell Count Is Associated With A Worsening Of Insulin Sensitivity And Predicts The Development Of Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes
High White Blood Cell Count Is Associated With A Worsening Of Insulin Sensitivity And Predicts The Development Of Type 2 Diabetes Diabetes
It may also be a sign of physical or emotional stress.
Elevated white blood cells. Pregnancy can also cause a high or slightly elevated white blood cell count. It may also means it is a reaction to a drug that helps in improving the WBC production. Neutrophils lymphocytes monocytes eosinophils and basophils.
If your test results show an elevated white blood cell count your first thought might be that something horrible is wrong with you. Here is a list of diseases and disorders which can raise the WBC count of an individual. A reaction to a drug that increases white blood cell production.
In addition to your total white blood cell count InsideTracker also measures the different types of white blood cells which can give clues as to what may be causing the elevated white blood cell count. The types of white blood cells include. Slightly elevated white blood cell count usually indicates an infection a problem in the immune system or bone marrow or it can be a side-effect of a drug.
In early March of 2018 my rheumatologist ran some routine blood work. Over the last few years my white blood count has ranged from 12k-24k. An elevated white blood cell count could be caused by a viral bacterial or a parasitic infection.
An increased production of white blood cells to fight an infection. Myelodysplastic syndrome MDS is a condition affecting the white blood cells in your bone marrow. For instance slightly elevated white blood cell count should not worry you that much.
This is a normal immune-response to protect the body from pathogens. See the doctor if symptoms persist. When the body is fighting off infections the bone marrow works overtime to release more white blood cells.
An elevated white blood cell count is called leukocytosis and can be evidence that your body is trying to fight off something. However it should never be ignored. High WBC count usually means there is increase in production of these cells to fight a possible infection.
High white blood cells can mean anything from cancer to something mere like an infection. Neutrophils lymphocytes monocytes eosinophils and basophils. An elevated white blood cell count always signifies your immune system is working harder than usual.
The body produces too many immature cells called blasts. In case of increased count of WBCs usually an increase in one type of white blood cells is noticed. The blasts multiply and crowd out the.
Having a high white blood cell count and lupus is not something you hear about often. There are also other factors that can cause high white blood cells to count in cancer patients. Leukocytosis is a condition in which the white cell leukocyte count is above the normal range in the blood.
This could happen simply because your body is preparing for pregnancy or it could be your bodys response to a seasonal allergy cold or flu or even strenuous exercise and emotional stress. It is frequently a sign of an inflammatory response most commonly the result of infection but may also occur following certain parasitic infections or bone tumors as well as leukemia. Usually blood test results show elevated white blood cell count if you are fighting an infection or have an inflammatory condition.
Bone marrow diseases may also cause high white blood cells count. However there are lots of potential causes and slightly elevated levels are usually not a cause for concern. This disorder is not common and causes anaemia fatigue enlarged spleen and severe anaemia.
The exact threshold for a high white blood cell count varies from one laboratory to another. This disease is characterised by bone pain excessive sweating at night easy bruising and bleeding. Counts around 30000 can be due to physical stress injuries allergic reactions infections or medication.
A high white blood cell count usually indicates. Any WBC count higher than 11000 white blood cells per cubic millimeter is considered high. Myelofibrosis is a bone marrow disorder that may lead to high white blood cell count.
A bone marrow disorder is a less common more serious cause of elevated white blood cells. An immune system disorder that increases white blood cell production. A high white blood cell count may indicate that the immune system is working to destroy an infection.
People with particular blood cancers. In general for adults a count of more than 11000 white blood cells leukocytes in a microliter of blood is considered a high white blood cell count. Other bone marrow disorders such as polycythemia vera can also increase the WBC count.
Your white blood cell count can be affected by race and any existing health condition. However the general consensus is that a normal range is between 4500 to 10000 white blood cells per cubic millimeter. A disease of bone marrow causing abnormally high production of white blood cells.
With this type of cancer the bone marrow produces large numbers of defective white blood cells and releases them into the blood. Leukemia is the most frequent culprit. If your white blood cell count is elevated you should speak with your doctor.
An elevated white blood cell count can arise due to many medical reasons. This condition is known as leukocytosis. White blood cells can be divided into five main types.
A high white blood cell count is an increase in disease-fighting cells in your blood.
