1Enzyme production transcription and translation of enzyme genes can be enhanced or diminished by a cell in response to. Competitive inhibition occurs when molecules very similar to the substrate molecules bind to the active site and prevent binding of the actual substrate.
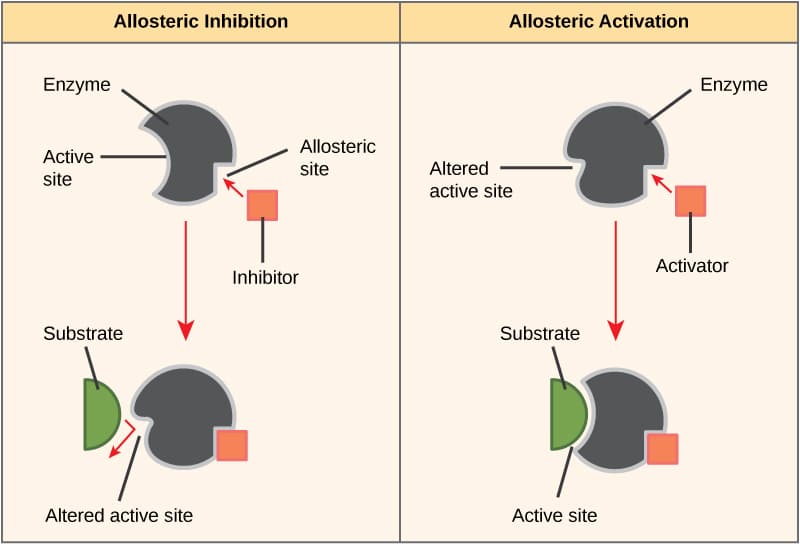 Enzyme Inhibition Types Of Inhibition Allosteric Regulation Teachmephysiology
Enzyme Inhibition Types Of Inhibition Allosteric Regulation Teachmephysiology
Enzyme activity is affected by various factors including substrate concentration and the presence of inhibiting molecules.

How can enzymes be inhibited. Weve seen previously how enzymes have a pH optimum. The latter occurs when the inhibitor binds tightly to the enzyme often covalently and dissociates very slowly from the target. Enzymes are regulated by controlling the level of transcription for them as well as inhibition.
The reversible inhibition on the other hand is characterized by a rapid dissociation of the enzymeinhibitor complex. Inhibition of enzyme by its substrate occurs when a dead-end enzyme-substrate complex forms. This inhibition of enzyme action is of a competitive nature because the inhibitor molecule actually competes with the substrate for.
This type of negative feedback slows the production line when products begin to build up and is an important way to maintain homeostasis in a cell. Enzymes are regulated by controlling the level of transcription for them as well as inhibition. Bonds between the strings of amino acids.
Enzyme inhibitors can roughly be classified into substrate analogs and transition state analogs. Enzymes Can Be Inhibited. The first way to inhibit an enzyme is to denature it.
Inhibition is when a compound or protein physically contacts the enzyme and reduces activity. Enzyme inhibition can be reversible or irreversible. For example enzymes in a metabolic pathway can be inhibited by downstream products.
The kinase enzymes cleave off a phosphate group from ATP and binds it to the enzyme. For example the end products of a metabolic pathway are often inhibitors for one of the first enzymes of the pathway usually the first irreversible step called committed step thus regulating the amount of end product made by the pathways. Some molecules very similar to the substrate for an enzyme may be bound to the active site but be unable to react.
There are roughly two types of inhibitors. An Enzyme Inhibitor is a molecule that reacts or binds with an enzyme molecule which causes a decrease in the activity of the enzyme. There Are Two Types Of Inhibition.
Special case of enzyme inhibition is inhibition by the excess of substrate or by the product. The rate of an enzymatic reaction increases with increased substrate concentration reaching maximum velocity when all active sites of the enzyme molecules are engaged. If the pH drops below or rises above that optimum then the secondary tertiary and quaternary bonds that stabilize the enzymes shape can change.
Phosphorylation provides another mechanism by which enzymes can be inhibited. Inhibition is when a compound or protein physically contacts the enzyme and reduces activity. This typically occurs through the action of kinase enzymes which can either inhibit or activate an enzyme depending on the situation.
Enzymes activity can be inhibited in a number of ways. Both types of analogs inhibit the enzyme via generally competing with the substrate for binding to the active site of the enzyme but are not affected by the enzyme. Enzyme activity can be inhibited in various ways.
There are five main ways that enzyme activity is controlled in the cell. A pH at which the enzymes active site has the specific 3-D shape for binding with its substrate. Competitive And Noncompetitive allosteric.
Protein - Protein - Inhibition of enzymes. Competitive inhibitors a molecule blocks the active site so that the substrate has to compete with the inhibitor to attach to the enzyme. This inhibition may follow the competitive uncompetitive or mixed patterns.
Inhibitors Can Slow Down Or Stop Enzymatic Reactions. Enzymes are long chains of amino acids that are folded into functional three-dimensional structures. Apart from what Phototroph mentioned in their answer competitive and non-competitive inhibition an enzyme can be activatedinhibited via covalent modification of the protein post-translational modification such as phosphorylation by protein kinases phosphorylation is the most common modification.
Enzymes can be either activated or inhibited by other molecules. Such molecules cover the active site and thus prevent the binding of the actual substrate to the site.